责任链模式–Spring AOP
责任链模式是一个链,链上分布着若该节点,当请求过来时,第一个节点处理,然后交给下个节点处理,一直到链结尾。
分析Spring AOP 责任链模式实现
1:在代码中声明Spring AOP切点时,会给目标类生成代理对象,同时生成责任链 (protected final List<?> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers;)
2:在调用目标方法时,会调入ReflectiveMethodInvocation中的proceed方法,开始责任链调用,此时,责任链已经生成,如下图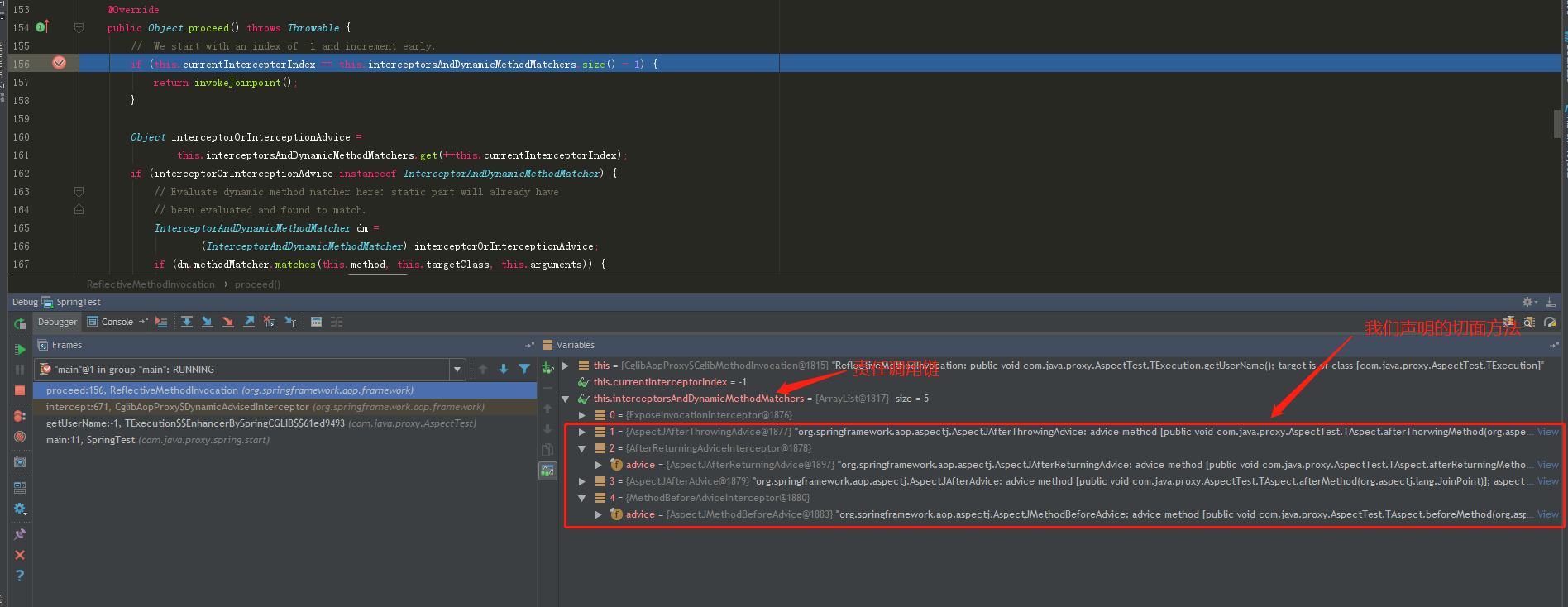
1 | /** |
*AOP 责任链默认排序 *
ExposeInvocationInterceptor – 把当前调用链名称放入ThreadLocal
AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice – 异常通知
AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor – 返回通知
AspectJAfterAdvice – 后置通知(如果前置通知或目标方法异常仍会执行)
MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor – 前置通知
递归调用流程如图: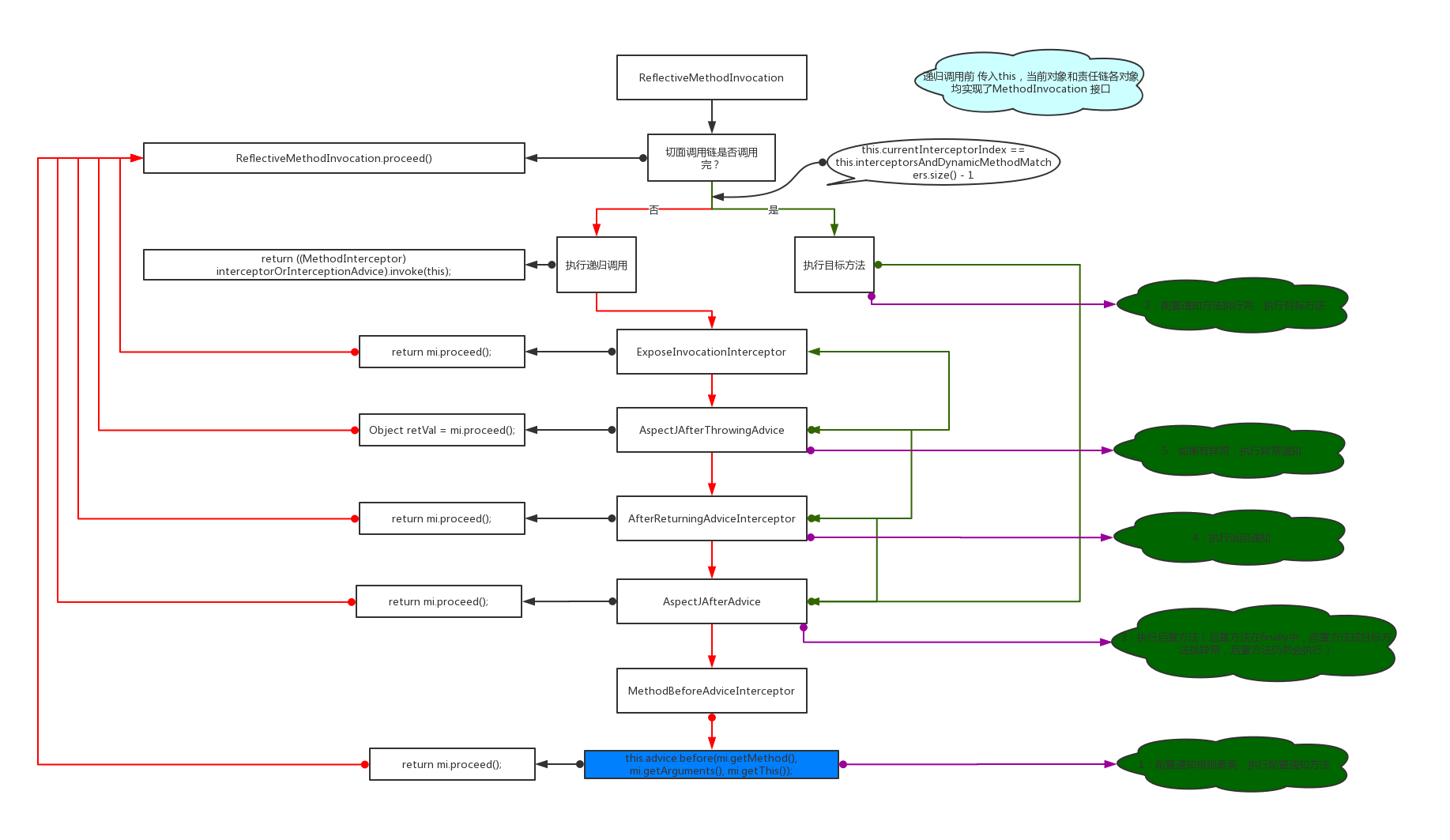
根据理解自己实现一个责任链
1:定义一个接口,各节点需要实现自己要做的事情
1 | package com.java.proxy.ResponsibilityChain; |
2:定义调用链封装
1 | package com.java.proxy.ResponsibilityChain; |
3:测试
1 | package com.java.proxy.ResponsibilityChain; |
结果:
第一个链执行。。。。
第二个链执行。。。。